Michigan, a state characterized by varied landscapes and cultures, faces notable challenges and transformations. Based on the 2020 census data, Michigan witnessed a 2% overall population growth from 2010 to 2020. However, the majority of its counties saw a decline in residents during the same timeframe.
How Does the Population Decline Affect These Counties?
A decrease in population can bring about various consequences for counties, including:
1. Economic Challenges: A workforce that is both smaller and older may result in diminished productivity, reduced tax revenue, and decreased public spending. This, in turn, can impact the quality and accessibility of services and infrastructure.
2. Social Issues: A population that is both declining and aging may contribute to feelings of isolation, loneliness, and health issues among the elderly. Additionally, it can widen the gap between different generations and cultures.
3. Environmental Impacts: While a shrinking population can alleviate pressure on natural resources and emissions, it may also heighten the risks of urban sprawl, land abandonment, and biodiversity loss.
It’s important to note that population decline isn’t inherently negative, but managing it effectively requires careful planning and adaptation to safeguard the well-being and sustainability of the affected counties.
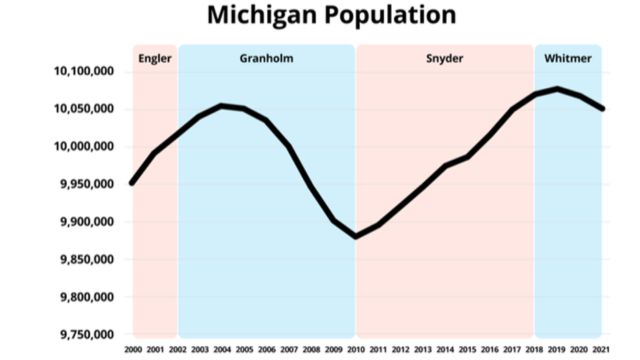
In this context, we will delve into the five Michigan counties that have encountered the most pronounced percentage-based population decrease, exploring the factors contributing to their diminishing numbers.
Luce County
Luce County, situated in the eastern Upper Peninsula, holds the distinction of being Michigan’s least populous county, boasting only 5,339 residents as of 2020. This marks a significant 19.5% decrease from the 2010 census, the most substantial decline among all Michigan counties.
The economic landscape of Luce County relies heavily on tourism, forestry, and agriculture. However, the region grapples with challenges such as aging infrastructure, limited access to healthcare, and a deficiency in broadband internet connectivity.
Moreover, the county faces the demographic challenge of a substantial elderly population. The potential departure or passing of these elderly residents, without a corresponding influx of younger generations, poses demographic concerns for the area’s future.
Read More: Exploring the 5 Counties in Minnesota With the Most Rapid Population Decline
Ontonagon County
Ontonagon County is located in the western Upper Peninsula, bordering Lake Superior. It currently has a population of 5,816, reflecting a 14.2% decrease since 2010.
The county’s history is intricately connected to the mining industry, which used to be a major source of employment for thousands and a key driver of local businesses.
However, the decline in mining, combined with the loss of manufacturing and timber jobs, has resulted in limited economic opportunities and a diminishing tax base for Ontonagon County. Additionally, the county faces challenges such as a lack of educational and recreational facilities, as well as a notable out-migration of young adults.
Read More: Exploring the 5 Counties in Pennsylvania With the Most Rapid Population Decline
Gogebic County
Gogebic County, situated in the western Upper Peninsula and adjacent to Wisconsin, has a population of 14,380, indicating a 12.5% decrease since 2010.
Historically, it thrived as a prominent hub for iron ore mining. However, the industry’s decline in the 1960s resulted in abandoned mines and environmental degradation.
The county is also home to a substantial Native American community, primarily belonging to the Lac Vieux Desert Band of Lake Superior Chippewa. Unfortunately, these residents often encounter discrimination and marginalization within the county.
Read More: Exploring the 5 Counties in Texas With the Most Rapid Population Decline
Isabella County
Isabella County, situated in the central Lower Peninsula, encompasses Mount Pleasant, the county’s largest city, and hosts the campus of Central Michigan University.
The population currently stands at 64,394, reflecting an 8.4% decline since 2010. This decrease is primarily linked to a reduction in enrollment at CMU, which has experienced a 24% drop in student numbers since 2010.
As the largest employer and economic catalyst in the county, CMU’s decline has had widespread repercussions on various businesses and services in the area.
Read More: Exploring the 5 Counties in Alaska With the Most Rapid Population Decline
Baraga County
Baraga County is situated in the western Upper Peninsula and is named after Bishop Frederic Baraga, a missionary known for his work among the Native Americans in the region. With a population of 8,158, there has been a 7.9% decrease since 2010.
The local economy of Baraga County relies on tourism, fishing, hunting, and forestry. However, the area faces challenges due to insufficient infrastructure, transportation, and industry.
Notably, Baraga County has a significant Native American population, primarily from the Keweenaw Bay Indian Community, which has its own government and culture.
Read More: Exploring the 5 Counties in Arkansas With the Most Rapid Population Decline
Conclusion
The five Michigan counties undergoing the most rapid population decline are situated in rural areas, grappling with diverse challenges like economic downturn, industrial decline, demographic shifts, and social issues.
Despite facing uncertainties, these counties possess distinctive strengths and opportunities. To address their decline, they may need to explore innovative approaches to attract and retain residents, diversify and rejuvenate their economies, and enhance overall quality of life.
Collaboration with neighboring counties, regions, and the state is crucial for addressing shared issues and exchanging best practices. These counties are not just integral to Michigan’s past but also play a pivotal role in shaping its future.










Leave a Reply