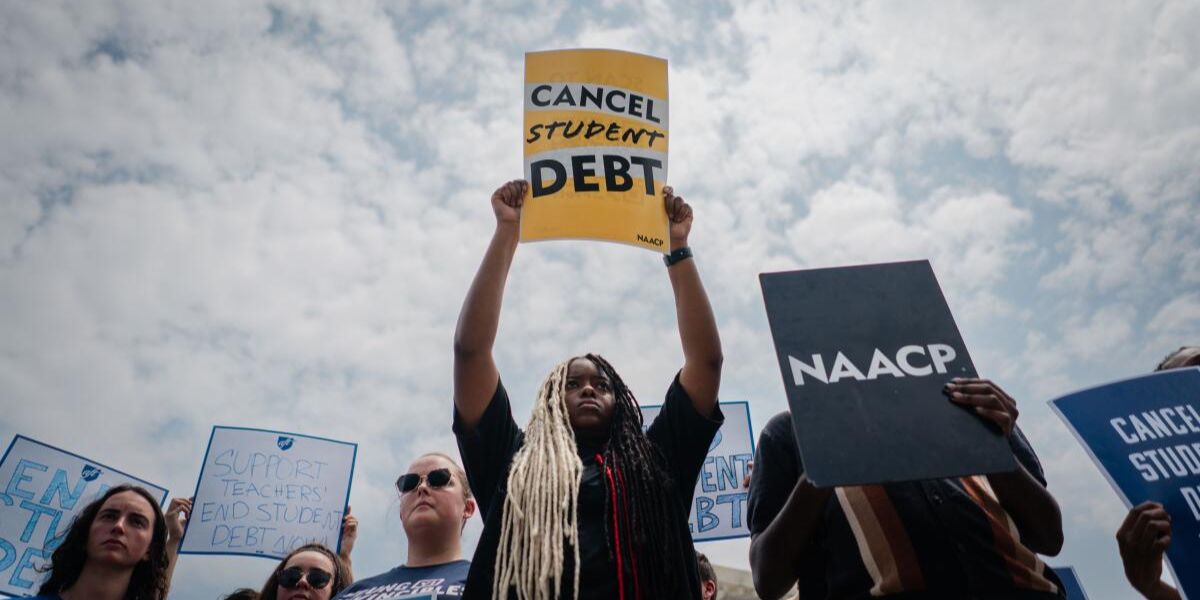
In October, the Biden administration hopes to unveil a fresh strategy for student loan forgiveness.
At least 25 million borrowers might receive relief from the program, according to the Unified Agenda proposed rule schedule.
It’s interesting to note that a large number of these debtors may qualify for automatic forgiveness without submitting an application. Like earlier attempts, legal hurdles are anticipated to be encountered by this scheme.
Who may be eligible for the most recent Biden Student Loan program?
The four primary types of borrowers targeted by the new student loan forgiveness proposal are as follows:
- Debtors with Runaway Interest: Those who have incurred significant interest since beginning repayment may be forgiven up to $20,000 or more.
- Borrowers who are eligible but have not yet registered in other forgiveness programs, such as income-driven repayment or public service loan forgiveness, fall into this category.
- Extended Undergraduate and graduate students who started paying back their loans at least twenty years ago and twenty-five years ago, respectively, are the borrowers.
- Borrowers from low-financial-value programs are those who enrolled in schools that aren’t eligible for federal financial aid or in programs with subpar student outcome indicators.
Biden could try to deliver on sweeping student loan forgiveness weeks before election https://t.co/dvmxIDTSrM
— CNBC (@CNBC) July 10, 2024
One important aspect of the suggested approach is the automatic forgiveness clause. Without having to apply, many borrowers may be able to have their loans forgiven.
This is made feasible by the Department of Education’s National Student Loan Data System, which provides access to adequate information about borrowers, including when they initially began payments.
This might save millions of individual applications, which would speed up relief.
Read Also: Gas Stimulus Payment: Who Can Get a Tax Refund?
Legal Repercussions for Biden’s New Student Loan Scheme
Even with the new plan’s potential scope, legal challenges are anticipated. The Supreme Court halted the prior attempt at student loan forgiveness.
The Higher Education Act, which clearly gives the Secretary of Education the authority to waive federal student loan commitments, serves as the alternative legal basis for the new program. Opponents could, however, dispute this expansive interpretation, which could cause the plan to be delayed or blocked.
This strategy is being implemented just weeks before the 2024 presidential election, during a politically sensitive period.
The fate of the idea could be greatly affected by the election’s result.
Given that former President Donald Trump has previously attacked and pushed to abolish such programs, if he is elected, his administration may put an end to the forgiveness initiatives.









Leave a Reply